NASA's Planetary Science Division Funding and Number of Missions 2004 - 2020
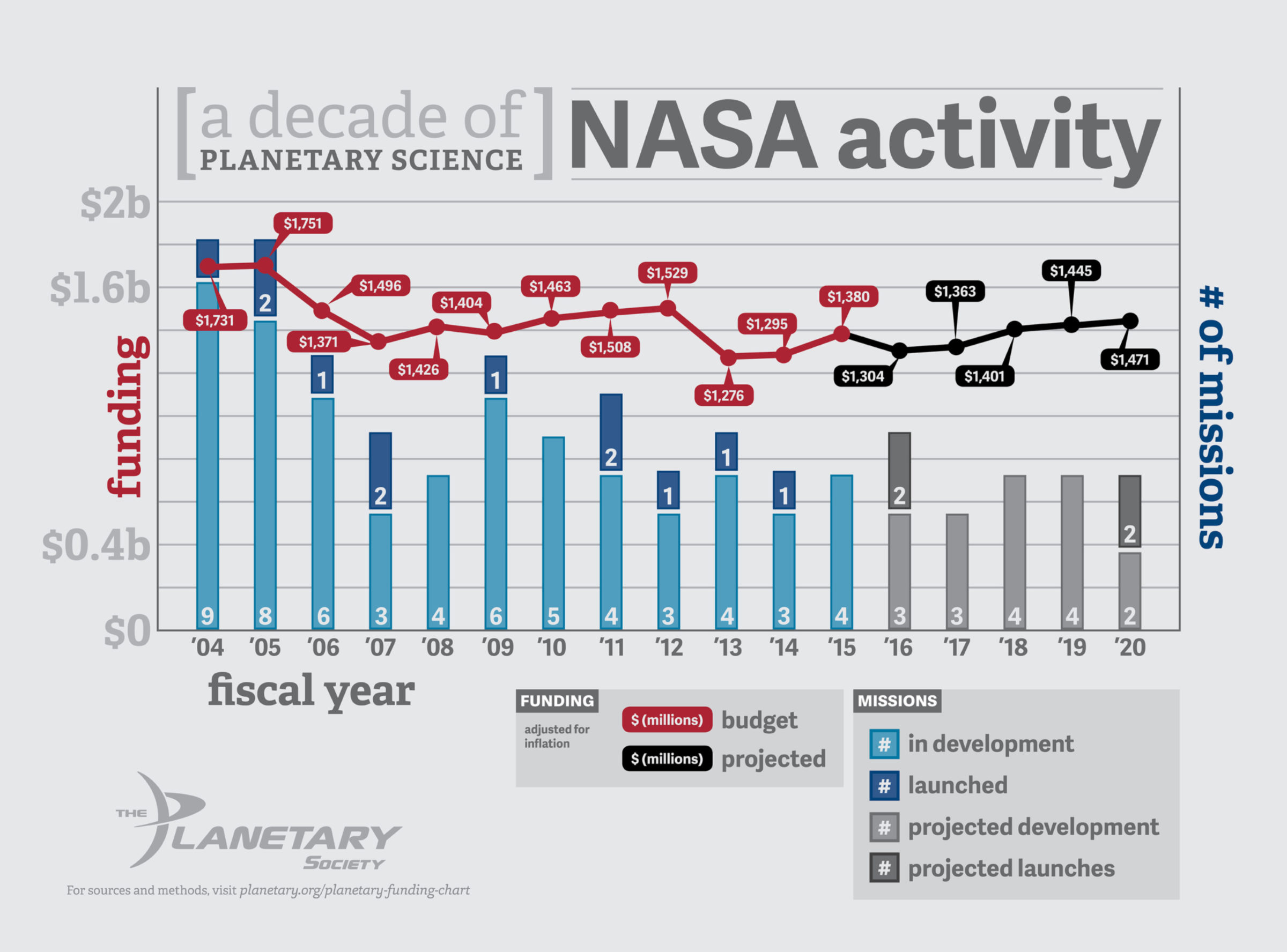
The above plot displays the overall budget of NASA's Planetary Science Division, which builds and maintains all solar system spacecraft. The large drop in funding in 2013 was due to the White House requesting major cuts to the program combined with the sequester.
Before the cuts (2003 - 2012):
- Average funding level was $1.51 billion per year.
- Average launch rate of 1.2 new mission per year.
After the cuts (2013 - 2019):
- Average funding level is $1.27 billion.
- Average launch rate is 0.57 new launches per year.
This means that NASA's Planetary Science Division suffers an average cut of $250 million, and its launch rate is cut in half. That means fewer missions of exploration and less science.
The Planetary Society advocates for a return to the historical level of funding for this program: $1.5 billion per year.
To learn more about what you can do to help reverse these cuts, visit our Be a Space Advocate section and contact your elected officials.
Data Details
Total amounts are adjusted for inflation and set to constant 2014 dollars according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics' CPI calculator. The years 2003 - 2013 are the actual amounts spent by NASA. The years 2014 and 2015 reflect the amount allocated to NASA for Planetary Science by Congress.
Total amounts are adjusted to retain programmatic consistency, in order to make a better "apples-to-apples" comparison:
- 2003 - 2005: Removed funding for NASA's Deep Space Network and combined separate funding lines for Mars and Solar System exploration activities.
- 2004: Removed funding for Project Prometheus.
- 2014 - 2015: Removed $50M for that is used to pay for the Department of Energy's Radioisotope Power Program infrastructure.
- 2016 - 2020: These numbers are from the White House's FY2016 NASA Budget request projections, from which $57.5M was removed to account for the funding transferred to the Department of Energy's Radioisotope Power Program infrastructure.
Future missions in development are (from the FY2015 Budget request):
- FY15: Mars 2020, InSight, OSIRIS-REx, Europa
- FY16: Mars 2020, Discovery 13, Europa (ORISIS-REx and InSight launch)
- FY17: Mars 2020, Discovery 13, Europa
- FY18 - FY19: Mars 2020, New Frontiers 4, Discovery 13, Europa
- FY20: Europa, New Frontiers 4 (Mars 2020 and Discovery 13 launch)
Raw data for this chart are located on this public Google Spreadsheet.


 Explore Worlds
Explore Worlds Find Life
Find Life Defend Earth
Defend Earth

