Emily Lakdawalla • Apr 08, 2009
Kepler's removed the lens cap
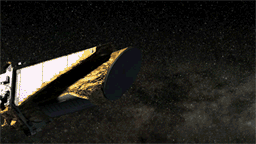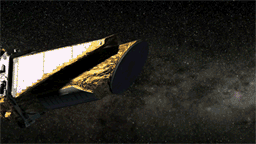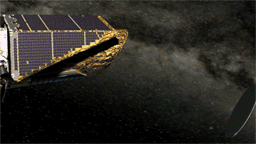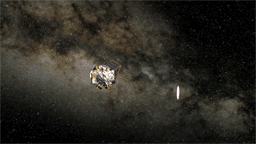
Since launch, Kepler's enormous photometer instrument, backed by a 42-Megapixel CCD (the largest such device ever sent to space by NASA), has been protected behind a truly gargantuan lens cap. The mission announced late yesterday that the lens cap (more correctly, "dust cover") was successfully ejected, first tipping to one side on a "flyaway hinge" and then springing off into space. Now the photometer can start collecting starlight. The release states they still have a few weeks of calibration work to do before science data gathering can begin.
NASA / Ames / JPL-Caltech
Kepler ejects its dust cover
On April 7, Kepler ejected the 1.7 - by - 1.3 - meter cover that had protected its sensitive photometer from dust since launch. With the cover removed, it could start collecting starlight. Download a high-resolution version of this animation here.Let’s Go Beyond The Horizon
Every success in space exploration is the result of the community of space enthusiasts, like you, who believe it is important. You can help usher in the next great era of space exploration with your gift today.
Donate Today

 Explore Worlds
Explore Worlds Find Life
Find Life Defend Earth
Defend Earth

